In this tutorial, we will learn what is a computer network? definition, components and everything you should know.
Overview
1) What is the advantage of computer network?
2) How many types of computer network?
3) Example of computer networks
4) Frequently used terms in internet
5) What is network topology?
6) What is OSI model (open system interconnection model)?
7) What is TCP / IP and how does it work?
8) What is protocol in computer network?
9) What is an IP addressing?
10) What is subnet addressing?
11) What are classes of IP address?
12) What are internet control protocols?
13) What are email protocols?
14) What are the IEEE 802 standards?
15) What are channel access methods?
16) What is CSMA?
17) What is CSMA / CD?
18) What is token passing?
19) What is ethernet?
20) What is token ring?
21) What are the LAN interconnecting devices?
Computer Network Full Tutorial | Computer Network Full Course with Proper Diagram
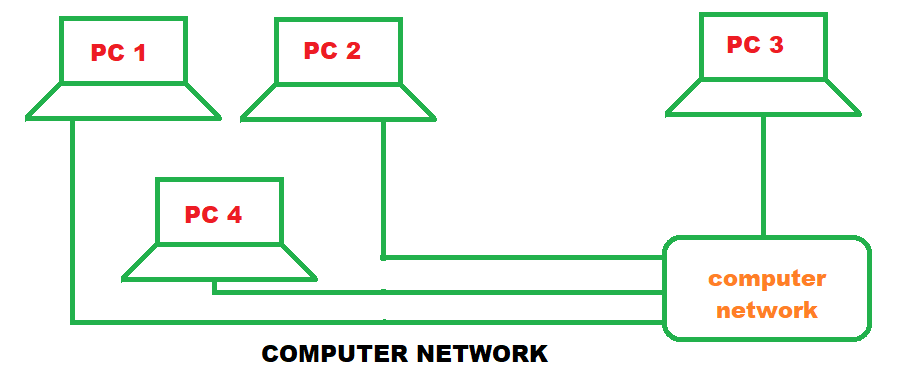
A computer network is a collection of computers and devices connected together via communication devices and transmission media.
For example - It may connect computer to many other computer printer scanner.
The medium of connection of communication device is optical fiber, co-axial fiber, wireless (radio wave, microwave and satellite).
The computer network can be arranged by some topology like ring, star, bus, hybrid.
What is the advantage of computer network?
- Sharing of device such as printer and scanner.
- Shading of program / software.
- Sharing of data.
- Sharing of information.
- Sharing of single high speed internet connection.
- Better communication using internet such as, email, mailing list and internet related chat.
How many type of computer network?
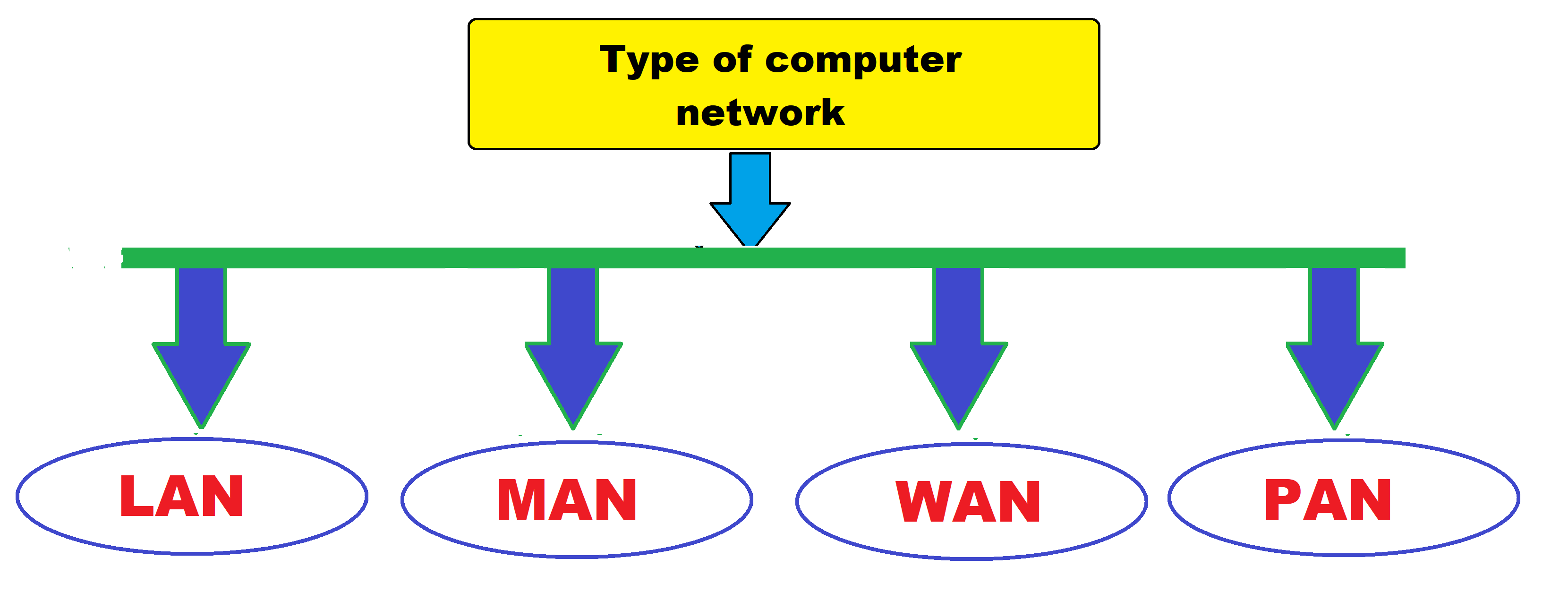
- L A N (Local area network)
- M A N (Metropolitan area network)
- W A N (Wide area network)
A) L A N (Local area network)
- A local area network is a network that connect computer and devices in a limited geographical area in the range of 500m to 1km.
- It is a small computer network that cover building or a campus.
- High bandwidth.
- They offer lower delay as they cover a smaller distance.
- Very high security.
- More than one LAN used in wide area network (W A N) to cover long distance.

B) M A N ( metropolitan area network )
- A metropolitan area network connect computer and devices in metro city in the range of 100 kilometer.
- A MAN typically include one or more LANs but it covered a small geographical area.
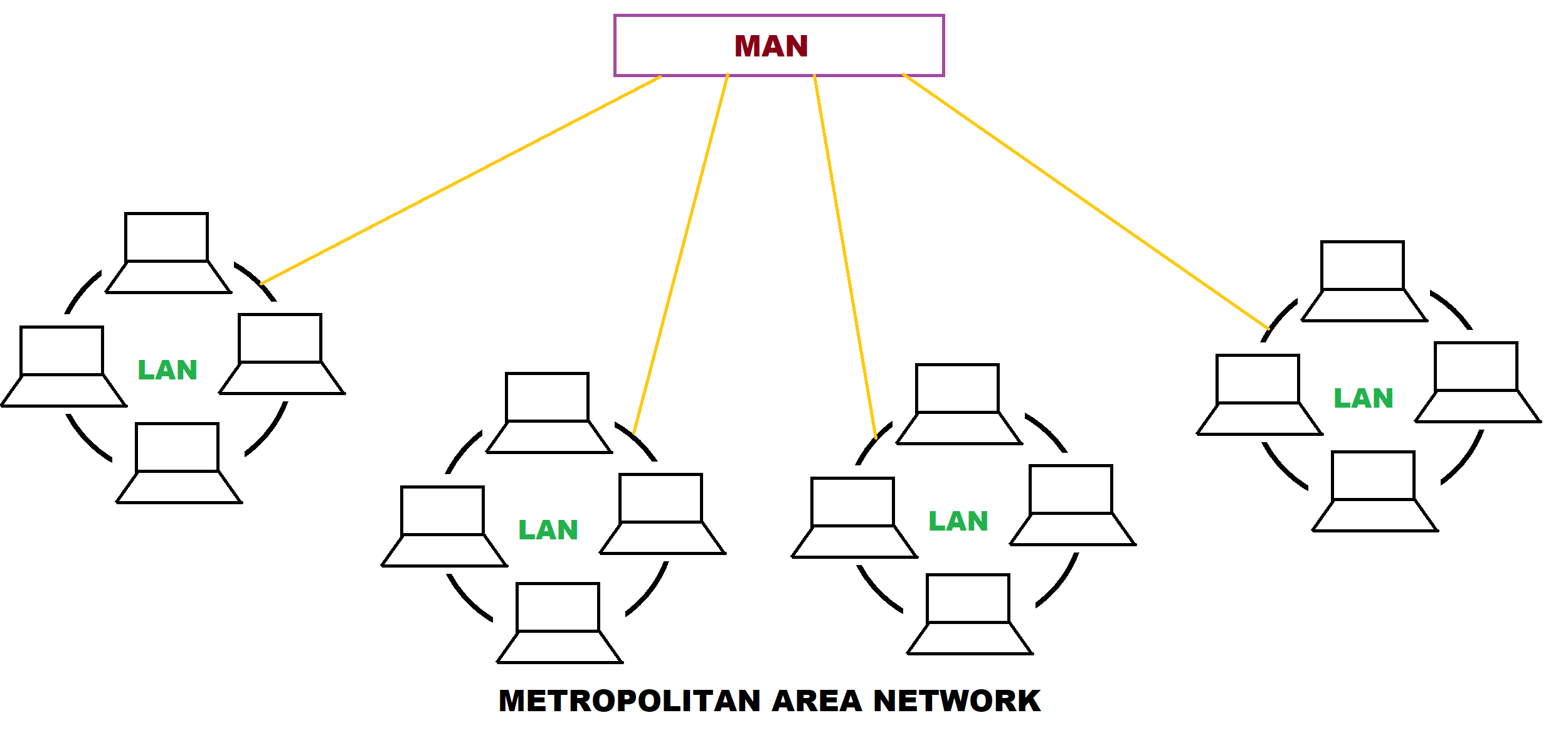
C) W A N ( Wide area network )
- A wide area network is a network that cover large geographical area such as a country or the world.
- WAN combines many type of media such as telephones line, cable and radio web.
- A WAN can be one of the largest network.
- WAN consist two or more LANs connect together.
- The internet is the world largest WAN.
- Low bandwidth.
- They offer much greater delays as they cover far distance.
- Security is high.

Example of computer networks :-
1) ARPANET
Full form of ARPANET is advanced research project as agency network. in earlier computer is used as a single machine and we cannot use internet. computer used to establish communication between different users.
ARPANET was design by advanced research agency (ARPA) for department of defence.
ARPANET was the first network in the world.
In 1969, the first ARPANET was established.
ARPANET was originally developed for long-distance (remote) computing. Remote computing was done by a utility program known as telnet. Which allow the user to connect one computer to another computer on a network.
2) Private network
Private network is a network that have specified network. Where many type of restrictions are established to create secure environment. In private network, the device outside the network does not connect. Only selected devices can access this type of network depending on setting of network return and access point.
Private network mostly used in business and private organization because they need high security for data / information.
Private network is complicated to setup. First we need to allow how many number of users or devices can be connect.
High security hardware and application like firewalls need to be install.
3) Internet
The internet or simply net is a worldwide network of computer network. It is a interconnection of large and small network around the world.
The internet is a public network which is accessed by anyone from any part of the world.
Working of internet
When we transfer any data through internet then it is broken into a lot of same size pieces called packet.
A header is added to each packets that explain where it come from and where it go.
Each packets is sent computer to computer until find its way to its destination. Each computer in the way decide where next to send the packet.
At the destination, the packets are examined, if there is any packet missing or damaged then a message sent to the sender for data to be resent.
Then the packets are reassembled into their original form.
Computer connect to the internet has a software called TCP / IP (transmission control protocol or internet protocol). Which is responsible for sending comedy saving and checking packets. IP / TCP is the glue of internet.
Frequently used terms in internet :-
1) World Wide Web (www)
The world wide Web (www) is a source of information in which document and other web resources are identified by uniform resource locator (URLs) and it is accessed via the internet.
2) Web page
Web page is a document which is basically.
written in hypertext markup language (HTML). That can be accessed through internet using any web browser. A web page is page with in a website.
3) Website
It is a collection of many web pages. we can also said that webpage may content text, image, audio and video, pdf etc.
4) Hyper text
The text having link is called hypertext. It is also called linked text. You can click on a hypertext to go to another web page or website.
5) HTTP
Hypertext transfer protocol enable the internet user to access the webpage placed in the website.
What is network topology?
Network topology used to explain the manner in which network is physically connected.
Type of network topology :-
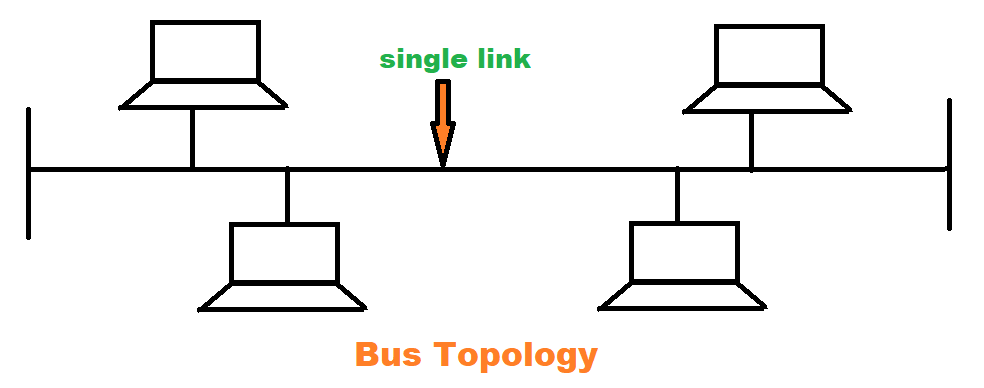
1) Bus Topology
- Multi point.
- Easy to install.
- Use for small network.
- Easy to expand.
- Slow speed and only one system can transmit at a time.
- Faulty cable bring down whole network.
2) Ring Topology
- In this is computer connect to the next computer and the last computer connect to first computer.
- Multiple data connection.
- Token passing is used.
- Fault in any link disable entire network.
- Difficult to troubleshoot the ring.

3) Star Topology
- All the wire from the computer go to a control location device called a HUB.
- All the communication goes through a HUB.
- If central HUB is failed then whole network fail.
- Cabling cost is more.

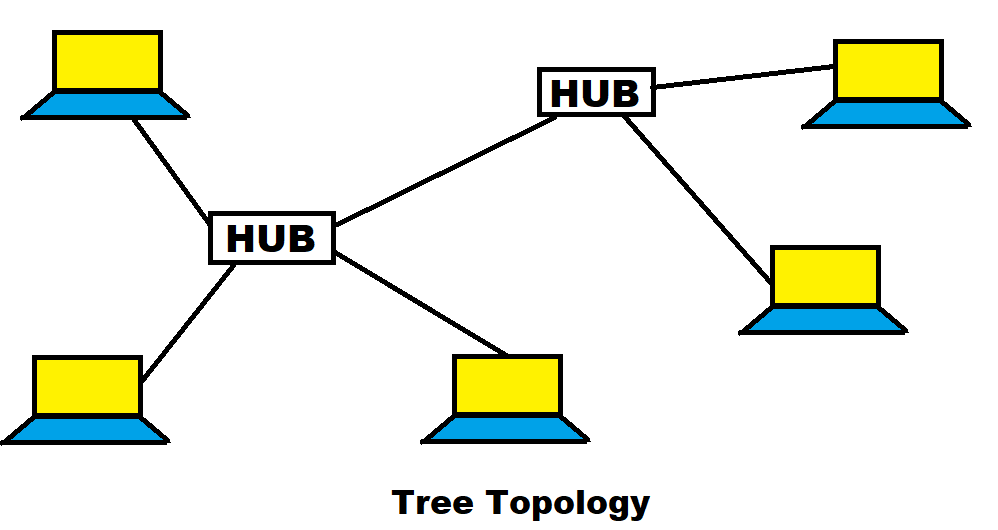
4) Tree Topology
- It is similar as star topology.
- Nodes in a tree topology are linked to a central HUB.
- Cabling cost is most.
- If control HUB is failed then entire network is fail.
5) Hybrid Topology
- Hybrid topology is a combination of two or more topologies (bus, comedy, star etc).
- Very easy to detect the fail system.
- Troubleshoot is easy.
- It include both wired and wireless network.
- Difficult to understand the network.
- Cost is high because required lot of cable and cooling system.
- M A U (multi station access unit) is required.

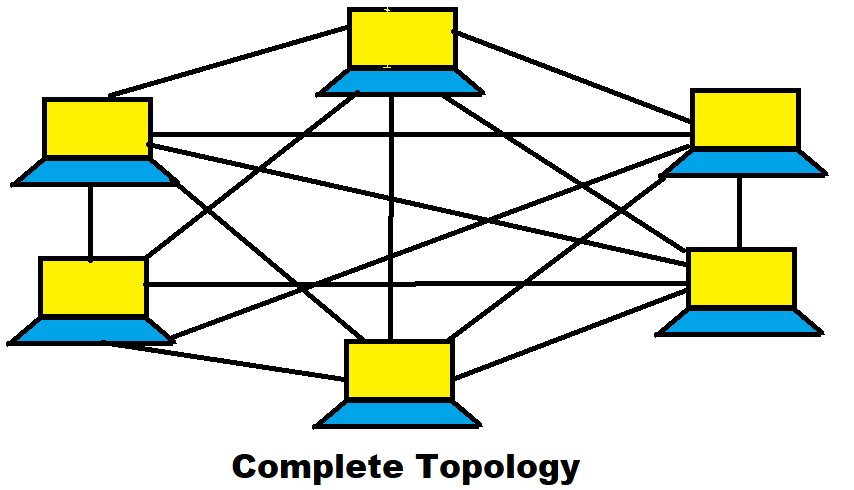
6) Complete Topology (mesh)
- In complete topology all the system connected to each other.
- High in cost because long wire required.
- It is basically used in workstation.
7) Irregular Network Topology
- An irregular network topology is similar to complete topology but in this topology not need to connect each computer to all the computer.
- The effect of failure depend on exact network topology.
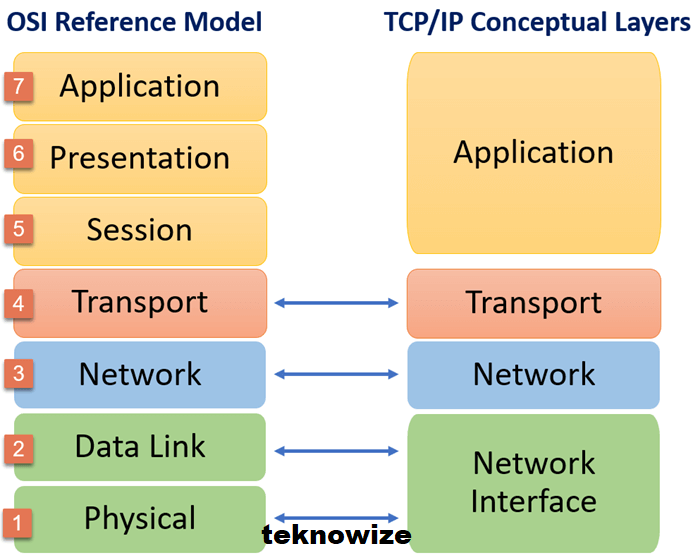
What is OSI model (open system interconnection model)?
OSI stand for open system interconnection. It has developed by ISO (international organization of standardization) in the year 1947.
It has seven layer architecture with each layer having their own function to perform. All these seven layer used to transmit data from one person to another across the world.
1) Physical Layer ( layer 1)
The lowest layer of OSI model is physical layer. It is responsible for actual physical conncetion between the devices. The physical layer contain information in the form of bits. when receiving data, this layer get the signal received and convert into 0 and 1 and sent to the data link layer.
Device used :- cable, HUB, repeater, fiber etc.
Protocol :- IEEE 802-11
2) Data Link Layer ( layer 2 )
The data link layer is responsible for delivery of the message, nodes to nodes. The packet received from network layer is further divided into frames.
Device use :- bridge, NIC (network interference card), 2 layer switch.
Protocol :- IEEE 802.3, HDLC, IEEE 802.5 .
3) Network Layer ( layer 3 )
Network layer work for transmission of data from one host/user to other user located in different network. Here data in packet form and network layer select shortest path to transmit the packet.
Device use :- router, B router, 3 layer switch.
Protocol :- IP, ipv4, IPv6, ICMP, IGMP.
4) Transport Layer ( layer 4 )
Transport layer provide service to application layer and take service from the network layer. It responsible for end to end delivery of complete message. The data in the transport layer is refer to as segment.
Device use :- Gateway, Firewalls .
Protocol :- TCP, UDP, SCTP.
5) Session Layer ( layer 5 )
This layer is responsible for establishment of connection, maintenance of session, authentication and also ensure its security.
Device use :- firewall
Protocol :- PAP, RPC
6) Presentation Layer ( layer 6 )
This layer deal with Syntax and semantics of the info exchange between two system.
Device use :- firewall
Protocol :- MIME, SSL
7) Application Layer ( layer 7 )
It enables the user to access the network.
Device use :- firewalls, gateway, PC, phones
Protocol :- DNS, HTTP, FTP, telnet, SMTP, POP
What is TCP / IP?
TCP stands for transmission control protocol. It is a set of networking protocol that allow two or more computer to communicate using internet. It is developed before OSI model.
It contain 4 layer but now it contain 5 layer.
Layer of TCP / IP model :-
1) Physical Layer (layer 1)
- It responsible for actual physical connection between the device.
- The physical layer contain information in the form of beats.
- No specific protocol.
2) Data Link Layer (layer 2)
- No specific protocol.
- The data link layer is responsible for delivery of the message from nodes to nodes.
- The packet received from network further divided into frames.
3) Network Layer (layer 3)
Network layer work for transmission of data from one host / user to other user located in different network.
Here data in packet form and network layer select shortest path to transmit the packet.
4) Transport Layer (layer 4)
It is possible for end to end delivery of complete message. The data in the transport layer is referred to as segment.
5) Application Layer (layer 5)
It enables the user to access the network. Device used PC, mobile etc. and protocols are HTTP, FTP, telnet, POP, SMTP etc.
What is protocol?
Protocol is a set of rules used in communication or ensure systematic and safe transfer of data over network. Everything we send or receive through the internet work according to protocols and all this protocols exist in seven layer of OSI model.
Type of protocol :-
a) Internet protocol (IP)
It is working with TCP. When we send data over internet is broken into many pieces called packet and these packets are reassembled by IP and convert into original form and send to destination address.
b) Transmission control protocol (TCP)
Transmission control protocol is used for communication over the network. In TCP data is broken into small packet and sent to the destination.

c) User datagram protocol (UDP)
It is same as TCP but it used for transfer small size data packet and these data packet are called datagram. It is also work with Internet protocol (IP). If any packet are missing then it does not send a message to sender for resent data and it continuously working with missing data packet.
In this UDP head and UDP data is 8 bytes each.
What is IP addressing?
It identify a network on internet. Using this we can find range of address in a network and total possible number of hosts / user on network. IP addresses is most important for communicate between two or more computer / device because IP address find the actual computer to communicate.
What is subnet addressing?
Subnet address in use to share same internet address to multiple network on autonomous system. The sub network capability of TCP / IP also make it possible to divide a sub network into multiple logical network.
For example - An organization can have a single internet network address that is known to user outside the organization, yet it can configure its network internally into departmental subnet.
| Network Address ( 8 bits ) | Local Host Address ( 24 bit ) | Local Host Address ( 24 bit ) |
| Network Address | Network Address | Host Address |
| 01111101 | 00001101 0100 | 1001 000011 |
What are IP address classes?
- IP address has five classes.
- A B C D E are the classes of IP address.
- IP address from first to three classes (A B & C) can use for host / user address.
- Class D use for multicast.
- class used for experimental purpose.
Class of IP address are :-
| Class | First Octet Value | Subnet Mask |
| A | 0 - 127 | 8 |
| B | 128 - 191 | 16 |
| C | 192 - 223 | 24 |
| D | 224 - 239 | - |
| E | 240 - 255 | - |
For IP address from class A, the first 8 bit (the first decimal number) represent the network part and remaining part be host / user part.
For example - 10.50.120.7 Here, the first number (10) represent network part and remaining 50.120.7 represent host part.
What are Internet control protocols?
Internet control protocols are rule for transmission of the data over the internet.

Internet control protocols are :-
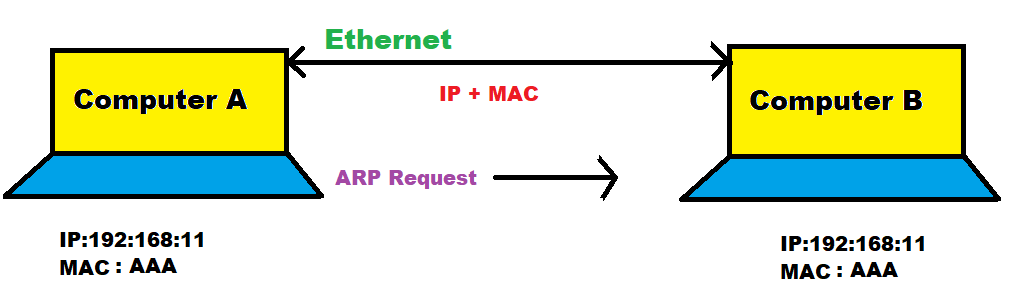
a) ARP
Address resolution protocol used when we want to communicate between one device to another device then, there should be each device has IP address (system address) but this IP address is not sufficient for communications so, the address resolution protocol request the Mac address of the other device then we communicate with each other.
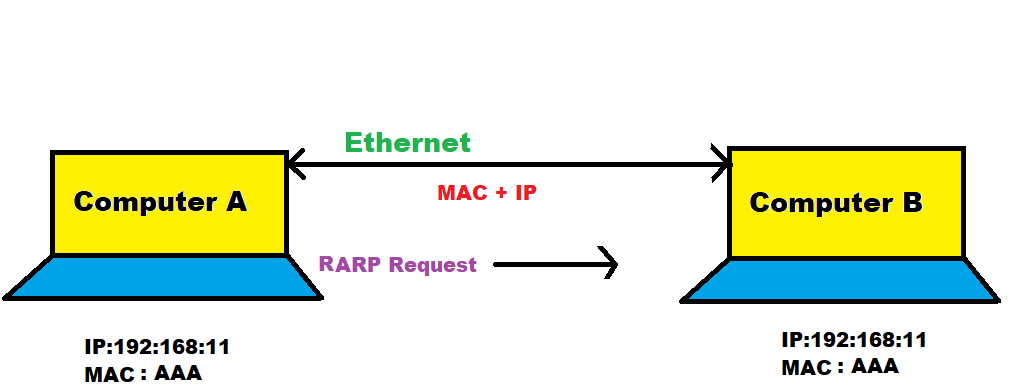
b) RARP
Reverse address resolution protocol used when we want to communicate between one device to another device then, the system know the Mac address of other system but do not know the IP address of another device so there RARP request IP address of the other device to communicate between them.
c) ICMP
Internet control message protocol is network diagnostic and error reporting protocol. ICMP belongs to IP protocol and it use IP as carrier protocol. If some error in network occur then it send message to origin host. ICMP contain dozens of diagnostic and error reporting message. It resolve the problem occur in Internet protocol like no error reporting.
Error reporting of ICMP are :-
- Destination
- unreachable time exceed
- Source quench
- Redirection
- Parameter problem
Message distributed by electronic means from one computer to one or more computer by the help of or via a network.
What are email protocols?
Email protocols are set of rules that help the client to properly transmit the information to or from the mail server.
We will discuss various protocols :-
1) SMTP
SMPT stand for simple mail transfer protocol. It is used for send mail. It is working under port 25.

SMTP comsmand-
- Hello - This command initiates the SMTP conversation.
- Mail from - This indicate the sender address.
- RCPT to - This indicate the receiver address on multiple receiver address.
- SIZE - Size of attached message in bytes.
- QUIT - The command is used to terminate the SMTP connection.
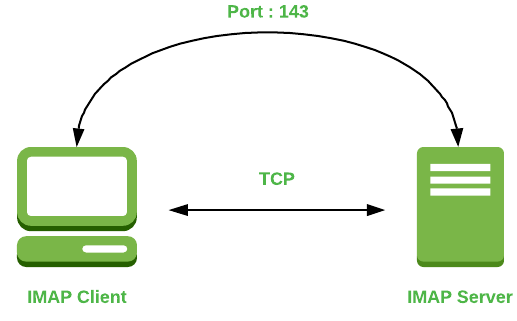
2) IMAP
IMAP stand for internet message access protocol. It is used to store mail in mail server (when we open mail like Gmail Yahoo, we can access all mail because this mail are store in mail server).
All the user request mail server to show their messages and then mail server ask to login with their own ID and password to access mail.
IMAP commands :-
- IMAP login - This command open the connection.
- SELECT - This command helps to select a mailbox to access the message.
- CREATE - It is used to create mailbox with specific name.
- DELETE - It is used to permanently delete mailbox.
- RENAME - It is used to change the name of a mailbox.
- LOGOUT - it is used to come out from the server and mailbox.
3) POP
It stand for post office protocol. It is used to receive mail from mail server using TCP / IP.

Currently used pop is POP3 fridge has version 3. POP support offline access to the message or required less internet.
POP commands :-
- LOGIN - this command open the connection.
- STAT - This used to display number of message currently in the mailbox.
- RETR - This command help to select a mailbox to access the message.
- DELE - It is used to delete a message.
- QUIT - It is used to log off the session.
- RSET - It is used to reset the session to initial stage.
What are IEEE 802 standards?
IEEE standard for institute of electrical and electronics engineering.
IEEE dealing with LAN and MAN.
The service and protocol specified in IEEE is lower two level of OSI model (data link layer and physical layer).
IEEE 802 splits the data link layer into sub layer.
- Logical link control (LLC)
- Media access control (MAC)
The most widely used standard is Ethernet, token ring, wireless LAN.
IEEE standard for LANs :-

Working group :-
- IEEE 802.1 - Standard for network management.
- IEEE 802.2 - Standard for logical link control sublayer of data link layer.
- IEEE 802.3 - Standard for Ethernet (MAC) media access control.
- IEEE 802.4 -Token bus network.
- IEEE 802.5 - Token ring network (MAC).
- IEEE 802.7 - Broadband LAN using coaxial cable.
- IEEE 802.8 - Fiber optic.
- IEEE 802.9 - Integrated service LAN ( ISLAN or ISO Ethernet).
- IEEE 802.11 - Wireless LAN (WLAN).
- IEEE 802.15 - Bluetooth.
What are channel access methods?
When many user try to access a channel then we apply some method called channel access method.
Channel access methods are :-
1) Aloha
Aloha are also called aloha method. It is simple communication scheme in which each source (transmitter) in a network send data where ever in a frame. If the frame successful is send then next frame is Sent. If frame fail to send then it need to resend.
There are two type of aloha :-
Pure aloha
Pure aloha in networking allowed the station to transmit the data at anytime and continuously.
In pure aloha station has sent continuously. There should be possibilities of collision due to continuous send data from station.
Pure aloha is also called continuous time system.
Continuous time system flow chart -

Working :-
Start and set back of time initially as 0 then send frame and acknowledgment from station. If an acknowledgment received than success. If acknowledgment not received then increment the back of time then check the limit reached or not, If yes then abort. If limit not reached then wait for a particular time and recent the frame again.
Slotted aloha
In slotted aloha user wait till the next station being to transmit the data.
It is discrete time system.
Efficiency :-
Efficiency of slotted aloha (x) = G * e-G
Where G = Number of station willing to transmit data at the beginning of the same time slot.
Maximum efficiency :-
Maximum efficiency of slotted aloha (x) = 36.8 % .
What is CSMA?
CSMA stand for carrier sensing multiple access.
CSMA is a network access method used on shared network topology.
There are three categories for CSMA :-
1) Non-persistence CSMA

In this user check only point of node for busy or free of channel.
If channel are busy then the station / user stop for a time and then recheck. In this there is a disadvantage that in the time in which user does not check for busy or free then high possibilities of chance of free of the channel.
2) I-persistence CSMA
In this user sense the channel continuously but in this also a disadvantage that in same time both user can transmit data and occurred collision.
3) P-persistence CSMA
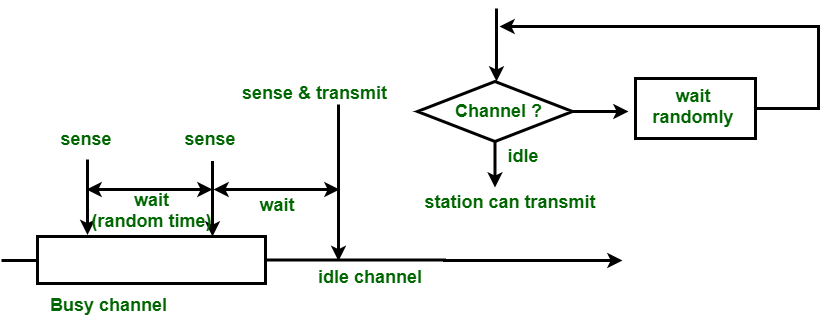
In this all the user check continuously but there should not all users sent data at same time. In these they send data first whose probability is high.
What is CSMA / CD?
Flow diagram :-

Theory :-
In this a station monitor the channel after it sent frame. If frame send successfully then station is finished work. After finished work if there is collision then frame need to recent.
What is token passing?
In this the station / node / computer in a network are create a logical ring.
In this method, a special packet call token. Data moving through the ring. In this token give rights to access the channel and send its data.
What is ethernet?
A system for connecting numbers of computer system to form a local area network with protocol to transfer or receive data by two or more system. It is mostly use LAN for linking computer together.
Mostly to type of ethernet are used :-
- Fast Ethernet
- Gigabit Ethernet
a) Fast Ethernet
Fast Ethernet is the successor of 10-Base-T Ethernet.
It is more popular than gigabit Ethernet because its configuration and implementation is simple. It is faster than its successor.
Its variants are :-
- 100 Base-T4
- 100 Base-Tx
- 100 Base-Fx
The coverage limit of fast Ethernet is up to 100 Km and its round trip delay in fast Ethernet is 100 to 500 bit times.
b) Gigabit Ethernet
Gigabit Ethernet is successor of first Ethernet. It can produce up to 1gbps speed. It is less popular than fast Ethernet because its configuration and implementation is complicated than fast Ethernet.
What is token ring?
- Token- token having data for transmission over network.
- In token ring method token passing through one node to another node by creating a logical ring.
- In this every node have predecessor node and successor note.
- In this token passing through one node to another node by creating a ring.
They are the four type of token ring :-
1) Physical ring
In this token passing through current node (which have data) to success node.
If there is fail in link then whole system fail.
There should not need any address.
2) Dual ring
In this there is two ring, one is clockwise and another is anticlockwise.
In this first ring is for original communication and second ring which move anticlockwise used for emergency (when first sync failed then emergency doing work).
If original ring should be repaired then emergency / secondary ring will stop work and then original ring will be come in working mode.
3) Bus ring
It is also called token bus. In this all station / node connect with single bus. A logical ring create for communication. Every node / station / system know the address of successor or predecessor node.
4) Star ring
Starting have star topology. This have a HUB and ring passing through one node to HUB then HUB to another.
In this all station / system / node connected with two wire. Chance of failure is less because HUB pass token.
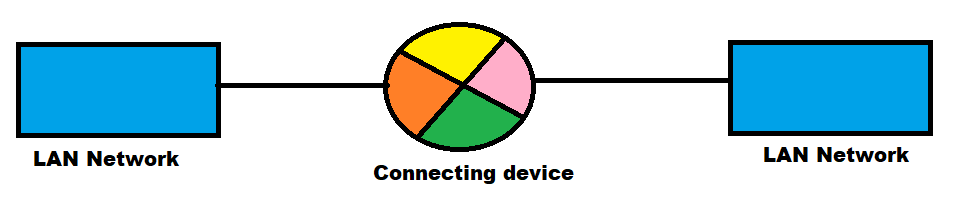
What are the LAN interconnecting devices?
A device which used to connect two LAN networks for communication is called connecting device.
There are many connecting devices work on different layer of OSI model :-

- HUB - working on physical layer.
- Bridge - working on physical and data link layer.
- Router - working on physical, data link and network layer.
1) HUB
This device work on only physical layer. So it is called 1 layer switch.

HUB is also called repeater. HUB is used because when we transfer data then due to long range signal will be week so we need to use HUB or repeater for regenerate the signal.
2) Bridge
Bridge work on physical layer and data link layer so it is known as 2 layers switch.

Bridge physical layer :-
Bridge work on physical layer as a repeater.
Bridge in data link layer :-
Bridge check the Mac address in the data link layer.
Note :- Bridge has a filtering capability by which if user send frame with destination address then the bridge decide to send the frame to the destination with suitable port.

3) Router
Router work on physical data link and network layer. So, it is known as 3 layer switch.

Router have physical and logical IP address for each of interface. router act as those address in which physical destination address match as address of the interface at which packet arrived.
4) Switch
Switch is used to communicate between two or more computer. It worked on data link layer. When we send data from one system to another system then the data passing through the switch and switch decide where to send data.

If we have more system and there is no port remaining then we need more switches to connect more system. In the below figure two switches are connected together with crossover cable.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Question - What is computer network and its uses?
Answer - A computer network is a collection of computer and devices connected together via communication device and transmission media.
Uses of computer network are :-
1) Sharing of device such as printer and scanner.
2) Shading of program / software.
3) Sharing of data.
4) Sharing of information.
5) Sharing of single high speed internet connection.
6) Better communication using internet such as, email, mailing list and internet related chat.
Question - What are the 4 types of networks?
Answer -
1) L A N (Local area network)
2) M A N (Metropolitan area network)
3) W A N (Wide area network)
4) P A N (Personal area network)
Question- Advantages of computer network?
Answer -
1) Sharing of device such as printer and scanner.
2) Shading of program / software.
3) Sharing of data.
4) Sharing of information.
5) Sharing of single high speed internet connection.
6) Better communication using internet such as, email, mailing list and internet related chat.
Question - What is LAN (Local Area Network)?
Answer -
- A local area network is a network that connect computer and devices in a limited geographical area in the range of 500m to 1km.
- It is a small computer network that cover building or a campus. High bandwidth.
- They offer lower delay as they cover a smaller distance.
- Very high security.
- More than one LAN used in wide area network (W A N) to cover long distance.
Question- What is MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)?
Answer -
- A metropolitan area network connect computer and devices in metro city in the range of 100 kilometer.
- A MAN typically include one or more LANs but it covered a small geographical area.
Question - What is WAN (Wide Area Network)?
Answer -
- A wide area network is a network that cover large geographical area such as a country or the world.
- WAN combines many type of media such as telephones line, cable and radio web.
- A WAN can be one of the largest network.
- WAN consist two or more LANs connect together.
- The internet is the world largest WAN.
- Low bandwidth.
- They offer much greater delays as they cover far distance.
- Security is high.
Question - What is ARPANET?
Answer - Full form of ARPANET is advanced research project as agency network. in earlier computer is used as a single machine and we cannot use internet. computer used to establish communication between different users.
Question - What is Internet?
Answer -
- The internet or simply net is a worldwide network of computer network.
- It is a interconnection of large and small network around the world.
- The internet is a public network which is accessed by anyone from any part of the world.
Question - How Internet works?
Answer - When we transfer any data through internet then it is broken into a lot of same size pieces called packet. A header is added to each packets that explain where it come from and where it go. Each packets is sent computer to computer until find its way to its destination. Each computer in the way decide where next to send the packet. At the destination, the packets are examined, if there is any packet missing or damaged then a message sent to the sender for data to be resent. Then the packets are reassembled into their original form. Is computer connect to the internet has a software called TCP / IP (transmission control protocol or internet protocol). Which is responsible for sending comedy saving and checking packets. IP / TCP is the glue of internet.
Question - What is World Wide Web (www)?
Answer- The world wide Web (www) is a source of information in which document and other web resources are identified by uniform resource locator (URLs) and it is accessed via the internet.
Question - How many type of network topology?
Answer -
Basically 7 type of network topology which basically use.
1) Bus Topology
2) Ring Topology
3) Star Topology
4) Tree Topology
5) Hybrid Topology
6) Complete Topology (mesh)
7) Irregular Topology
Question - What is OSI Model?
Answer- OSI stand for open system interconnection. It has developed by ISO (international organization of standardization) in the year 1947. It has seven layer architecture with each layer having their own function to perform. All these seven layer used to transmit data from one person to another across the world.
Question - What is Protocol?
Answer - Protocol is a set of rules used in communication or ensure systematic and safe transfer of data over network. Everything we send or receive through the internet work according to protocols and all this protocols exist in seven layer of OSI model.
Question - Types of Protocol?
Answer -
1) Internet protocol (IP)
2) Transmission control protocol (TCP)
3) User datagram protocol (UDP)
Question - What is IP addressing?
Answer - It identify a network on internet. Using this we can find range of address in a network and total possible number of hosts / user on network. IP addresses is most important for communicate between two or more computer / device because IP address find the actual computer to communicate.
Question- What is Subnet addressing?
Answer - Subnet address in use to share same internet address to multiple network on autonomous system. The sub network capability of TCP / IP also make it possible to divide a sub network into multiple logical network. For example - An organization can have a single internet network address that is known to user outside the organization, yet it can configure its network internally into departmental subnet.
Question - How many types of internet control protocol?
Answer-
1) ARP
2) RARP
3) ICMP
Question - What is HUB?
Answer - This device work on only physical layer. So it is called 1 layer switch. HUB is also called repeater. HUB is used because when we transfer data then due to long range signal will be week so we need to use HUB or repeater for regenerate the signal.
Question - What is Switch?
Answer- Switch is used to communicate between two or more computer. It worked on data link layer. When we send data from one system to another system then the data passing through the switch and switch decide where to send data.If we have more system and there is no port remaining then we need more switches to connect more system.